Laravel’s session blocking prevents race conditions and data inconsistencies by controlling concurrent session access. This feature ensures data integrity during simultaneous operations.
Understanding Session Blocking
Session blocking requires:
- Cache driver supporting atomic locks (redis, memcached, dynamodb, database)
- Non-cookie session driver
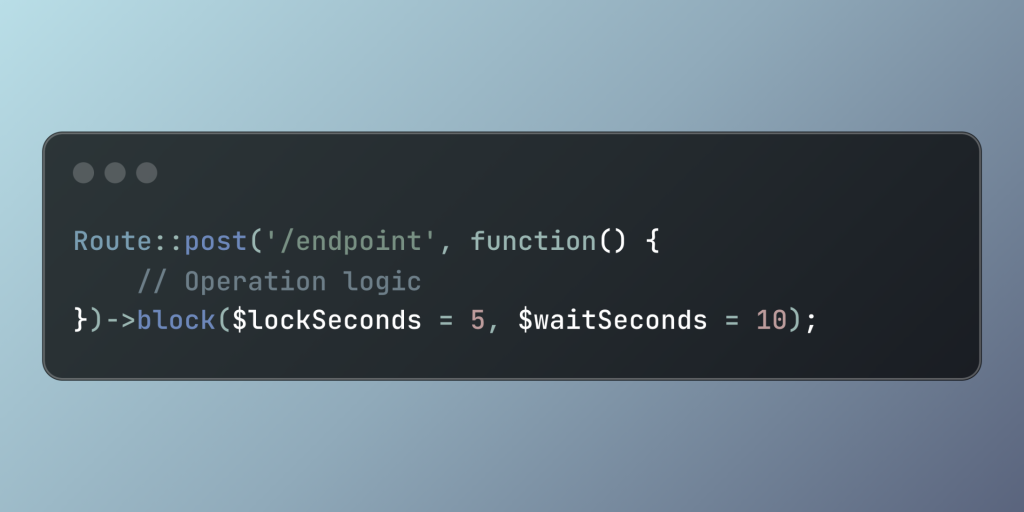
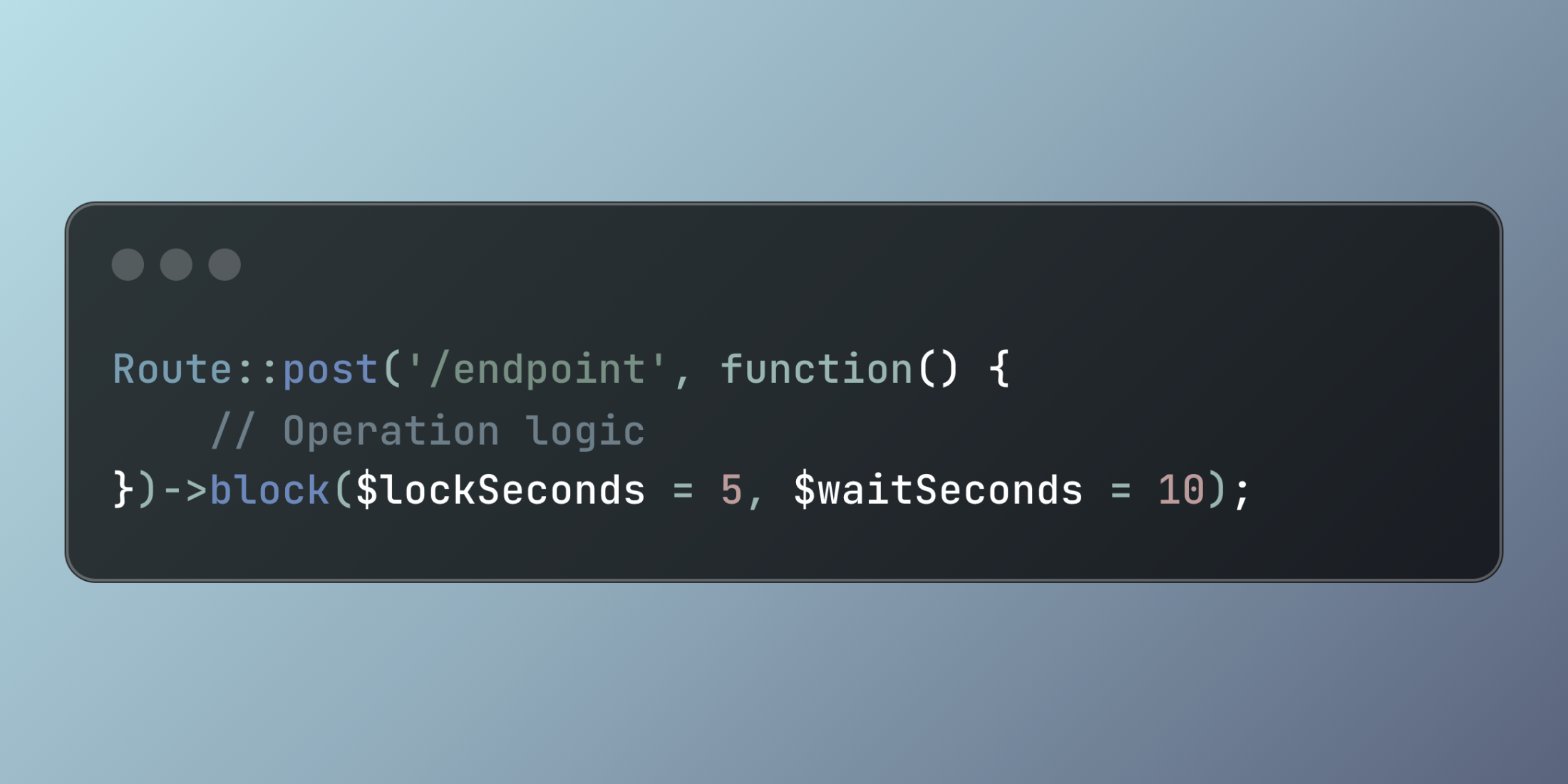
Route::post('/endpoint', function() {
// Operation logic
})->block($lockSeconds = 5, $waitSeconds = 10);
Real-World Implementation
Let’s build a payment processing system with concurrency control:
<?php
namespace AppHttpControllers;
use AppModelsPayment;
use IlluminateSupportFacadesDB;
use AppExceptionsPaymentException;
class PaymentController extends Controller
{
public function process(Request $request)
{
return DB::transaction(function() use ($request) {
// Validate payment exists and isn't processed
$payment = Payment::findOrFail($request->payment_id);
if ($payment->isProcessed()) {
throw new PaymentException('Payment already processed');
}
// Process payment
$result = $this->paymentGateway->charge([
'amount' => $payment->amount,
'currency' => $payment->currency,
'token' => $request->payment_token
]);
$payment->markAsProcessed($result->transaction_id);
return response()->json([
'status' => 'success',
'transaction_id' => $result->transaction_id
]);
});
}
}
// routes/api.php
Route::post('/payments/process', [PaymentController::class, 'process'])->block(5, 10);
This implementation:
- Prevents duplicate payment processing
- Waits up to 10 seconds for lock acquisition
- Uses database transactions for atomicity
- Handles concurrent requests gracefully
Session blocking provides a robust solution for managing concurrent requests, ensuring data integrity in high-traffic applications while maintaining a clean, Laravel-centric implementation.
The post Managing Concurrent Requests with Laravel Session Blocking appeared first on Laravel News.
Join the Laravel Newsletter to get all the latest
Laravel articles like this directly in your inbox.
Source: Read MoreÂ