Mental health profoundly impacts individuals’ quality of life, yet accessing mental health services can be challenging due to stigma, insufficient workforce, and fragmented care systems. NLP has demonstrated its potential in this area, with models developed to detect symptoms and evaluate depression from clinical texts. Language models like BERT have also been adapted for classifying mental disorders. However, creating these models requires substantial computational power, which many organizations need more, and regulations such as HIPAA and GDPR further complicate using cloud-based resources.
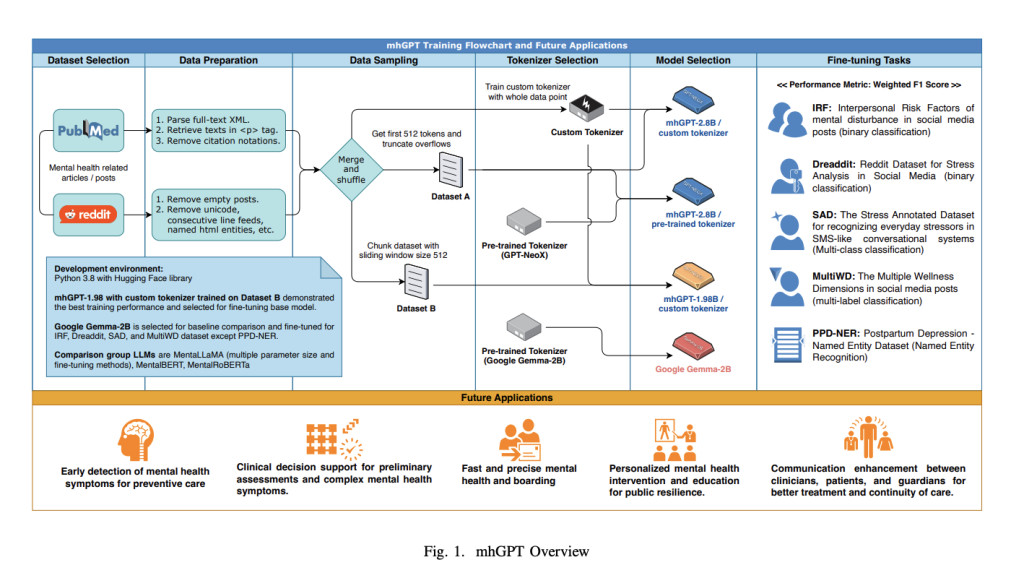
Children’s National Hospital and George Washington University researchers introduced mhGPT, a lightweight generative model trained on mental health-related social media and PubMed articles. Designed for low-resource environments, mhGPT, with only 1.98 billion parameters, outperformed larger models like MentaLLaMA and Gemma despite using just 5% of the dataset. The model benefits from integrating diverse mental health data and a custom tokenizer, showing that smaller, expert knowledge-infused models can match or exceed the performance of state-of-the-art models in mental health tasks, even with limited computational resources.
Few studies have developed mental health LLMs, primarily training them on social media data. MentaLLaMA, trained on the interpretable mental health instruction dataset, enhances zero/few-shot mental health analysis. MentalBERT focuses on the early detection of mental disorders and suicidal ideation from social content, outperforming general language models in this domain. Additionally, fine-tuned BERT models on EHR data for specific mental disorders, showing the benefits of domain-specific knowledge transfer. Fine-tuning remains essential for improving LLM performance, with methods like LoRA and QLoRA enabling efficient fine-tuning in low-resource environments by reducing memory usage and training time.
The study utilized 49,812 PubMed Central articles on mental health and over 1 million Reddit submissions and comments from various mental health subreddits. The data was preprocessed by removing irrelevant content and then sampled using two methods: truncating to 512 tokens or chunking with a sliding window. The training involved three configurations using the GPT-NeoX architecture with different parameter sizes and tokenizers. The models were trained on high-performance computing clusters and Amazon EC2 instances. Fine-tuning employed LoRA and QLoRA techniques, with NEFTune applied to mitigate overfitting, particularly in imbalanced datasets.
The study found that mhGPT outperformed comparable models like MentaLLaMA, MentalBERT, and MentalRoBERTa on various tasks despite these models being trained on larger datasets. mhGPT outperformed human annotators in a Named Entity Recognition (NER) task. The baseline model, Gemma-2B, performed well in binary and multi-label classification but may lack interpretability in mental health contexts. NEFTune improved fine-tuning on small, imbalanced datasets, allowing mhGPT to surpass larger models like MentaLLaMA-7B. Models A and B also showed strong performance in specific classification tasks.
In conclusion, mhGPT is a compact generative pre-trained transformer designed for mental health text analysis. Trained on mental health-related social media and PubMed articles, mhGPT was fine-tuned on five specific tasks and outperformed state-of-the-art models like MentaLLaMA despite having fewer parameters and training data. Key innovations include using expert knowledge-infused data, a custom tokenizer, and NEFTune for improved performance on imbalanced datasets. The study demonstrates mhGPT’s potential to enhance mental health AI, especially in low-resource settings, by optimizing a smaller model architecture.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. If you like our work, you will love our newsletter..
Don’t Forget to join our 48k+ ML SubReddit
Find Upcoming AI Webinars here
The post mhGPT: Advancing Mental Health AI with a Lightweight, Expert Knowledge-Infused Transformer for Low-Resource Environments appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ