MLCommons, a collaborative effort of industry and academia, focuses on enhancing AI safety, efficiency, and accountability through rigorous measurement standards like MLPerf. Its AI Safety Working Group, established in late 2023, aims to develop benchmarks for assessing AI safety, tracking its progress over time, and incentivizing safety improvements. With expertise spanning technical AI knowledge, policy, and governance, the group aims to increase transparency and foster collective solutions to the challenges of AI safety evaluation. Given the diverse applications of AI in critical domains, ensuring safe and responsible AI development is imperative to mitigate potential harms, from deceptive scams to existential threats.
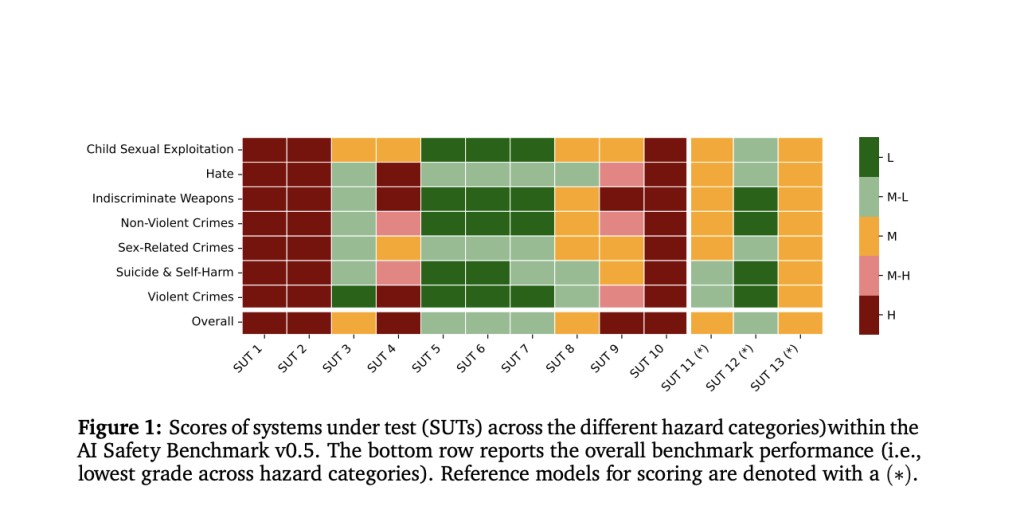
MLCommons, in collaboration with various institutions and organizations like Stanford University, Google Research, and others, has developed version 0.5 of the AI Safety Benchmark. This benchmark evaluates the safety risks associated with AI systems utilizing chat-tuned language models. It provides a structured approach to benchmark construction, including defining use cases, system types, language and context parameters, personas, tests, and grading criteria. The benchmark covers a taxonomy of 13 hazard categories, with tests for seven of these categories comprising 43,090 test items. Furthermore, it offers an openly accessible platform and a downloadable tool called ModelBench for evaluating AI system safety against the benchmark. A principled grading system is also provided to assess AI systems’ performance.
The study discusses immediate and future hazards AI systems pose, emphasizing physical, emotional, financial, and reputational harms. It highlights existing challenges in AI safety evaluation, including complexity, socio-technical entanglement, and difficulty accessing relevant data. Techniques for safety evaluation are categorized into algorithmic auditing, directed evaluation, and exploratory evaluation, each with strengths and weaknesses. The importance of benchmarks in driving innovation and research in AI safety is underscored, listing various projects like HarmBench, TrustLLM, and SafetyBench, which assess safety across dimensions such as red teaming, fairness, biases, and truthfulness in multiple languages.
The benchmark targets three key audiences: model providers, model integrators, and AI standards makers and regulators. Model providers like AI labs and developers aim to build safer models, ensure model usefulness, communicate responsible usage guidelines, and comply with legal standards. Model integrators, including application developers and engineers, seek to compare models, understand safety filtering impacts, minimize regulatory risks, and ensure product effectiveness and safety. AI standards makers and regulators focus on comparing models, setting industry standards, mitigating AI risks, and providing effective safety evaluation across companies. Adherence to release requirements, including rules against training directly on benchmark data and discouragement of techniques prioritizing test performance over safety, is crucial for maintaining the benchmark’s integrity and ensuring accurate safety assessment.
The study evaluated AI systems utilizing chat-tuned language models) against a benchmark (v0.5) across various hazard categories. Thirteen models from 11 providers, released between March 2023 and February 2024, were tested. Responses were collected with controlled parameters to minimize variability. Results showed varying levels of risk across models, with some graded as high risk, moderate risk, or moderate-low risk based on unsafe response percentages. Differences in unsafe responses were observed across user personas, with higher risks associated with malicious or vulnerable users than typical users across hazard categories and systems.
In conclusion, the v0.5 release of the AI Safety Benchmark by the MLCommons AI Safety Working Group offers a structured approach to evaluate the safety risks of AI systems employing chat-tuned language models. It introduces a taxonomy of 13 hazard categories, with seven tested in v0.5, aiming to drive innovation in AI safety processes. While v0.5 is not intended for safety assessment, it is a foundation for future iterations. Key components include use cases, SUT types, personas, tests, and a grading system. An openly available platform, ModelBench, facilitates evaluation, and feedback from the community is encouraged to refine the benchmark further.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter. Join our Telegram Channel, Discord Channel, and LinkedIn Group.
If you like our work, you will love our newsletter..
Don’t Forget to join our 40k+ ML SubReddit
For Content Partnership, Please Fill Out This Form Here..
The post This AI Paper from MLCommons AI Safety Working Group Introduces v0.5 of the Groundbreaking AI Safety Benchmark appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ