Advancements in artificial intelligence are rapidly closing the gap between digital reasoning and real-world interaction. At the forefront of this progress is embodied AI—the field focused on enabling robots to perceive, reason, and act effectively in physical environments. As industries look to automate complex spatial and temporal tasks—from household assistance to logistics—having AI systems that truly understand their surroundings and plan actions becomes critical.
Introducing RoboBrain 2.0: A Breakthrough in Embodied Vision-Language AI
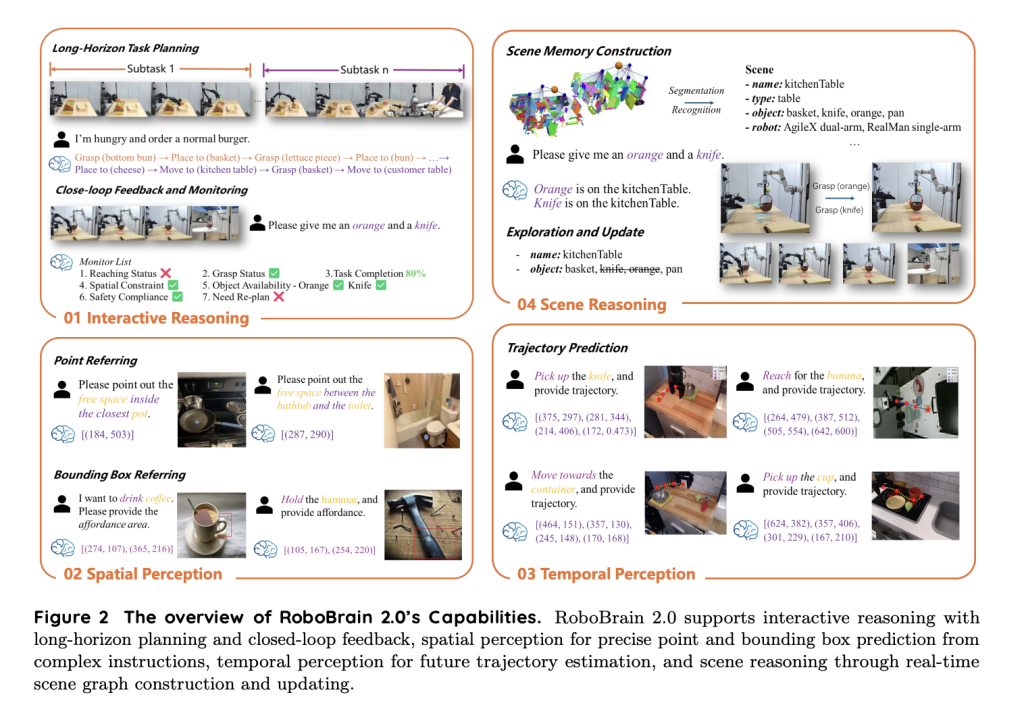
Developed by the Beijing Academy of Artificial Intelligence (BAAI), RoboBrain 2.0 marks a major milestone in the design of foundation models for robotics and embodied artificial intelligence. Unlike conventional AI models, RoboBrain 2.0 unifies spatial perception, high-level reasoning, and long-horizon planning within a single architecture. Its versatility supports a diverse set of embodied tasks, such as affordance prediction, spatial object localization, trajectory planning, and multi-agent collaboration.
Key Highlights of RoboBrain 2.0
- Two Scalable Versions: Offers both a fast, resource-efficient 7-billion-parameter (7B) variant and a powerful 32-billion-parameter (32B) model for more demanding tasks.
- Unified Multi-Modal Architecture: Couples a high-resolution vision encoder with a decoder-only language model, enabling seamless integration of images, video, text instructions, and scene graphs.
- Advanced Spatial and Temporal Reasoning: Excels at tasks requiring an understanding of object relationships, motion forecasting, and complex, multi-step planning.
- Open-Source Foundation: Built using the FlagScale framework, RoboBrain 2.0 is designed for easy research adoption, reproducibility, and practical deployment.
How RoboBrain 2.0 Works: Architecture and Training
Multi-Modal Input Pipeline
RoboBrain 2.0 ingests a diverse mix of sensory and symbolic data:
- Multi-View Images & Videos: Supports high-resolution, egocentric, and third-person visual streams for rich spatial context.
- Natural Language Instructions: Interprets a wide range of commands, from simple navigation to intricate manipulation instructions.
- Scene Graphs: Processes structured representations of objects, their relationships, and environmental layouts.
The system’s tokenizer encodes language and scene graphs, while a specialized vision encoder utilizes adaptive positional encoding and windowed attention to process visual data effectively. Visual features are projected into the language model’s space via a multi-layer perceptron, enabling unified, multimodal token sequences.
Three-Stage Training Process
RoboBrain 2.0 achieves its embodied intelligence through a progressive, three-phase training curriculum:
- Foundational Spatiotemporal Learning: Builds core visual and language capabilities, grounding spatial perception and basic temporal understanding.
- Embodied Task Enhancement: Refines the model with real-world, multi-view video and high-resolution datasets, optimizing for tasks like 3D affordance detection and robot-centric scene analysis.
- Chain-of-Thought Reasoning: Integrates explainable step-by-step reasoning using diverse activity traces and task decompositions, underpinning robust decision-making for long-horizon, multi-agent scenarios.
Scalable Infrastructure for Research and Deployment
RoboBrain 2.0 leverages the FlagScale platform, offering:
- Hybrid parallelism for efficient use of compute resources
- Pre-allocated memory and high-throughput data pipelines to reduce training costs and latency
- Automatic fault tolerance to ensure stability across large-scale distributed systems
This infrastructure allows for rapid model training, easy experimentation, and scalable deployment in real-world robotic applications.
Real-World Applications and Performance
RoboBrain 2.0 is evaluated on a broad suite of embodied AI benchmarks, consistently surpassing both open-source and proprietary models in spatial and temporal reasoning. Key capabilities include:
- Affordance Prediction: Identifying functional object regions for grasping, pushing, or interacting
- Precise Object Localization & Pointing: Accurately following textual instructions to find and point to objects or vacant spaces in complex scenes
- Trajectory Forecasting: Planning efficient, obstacle-aware end-effector movements
- Multi-Agent Planning: Decomposing tasks and coordinating multiple robots for collaborative goals
Its robust, open-access design makes RoboBrain 2.0 immediately useful for applications in household robotics, industrial automation, logistics, and beyond.
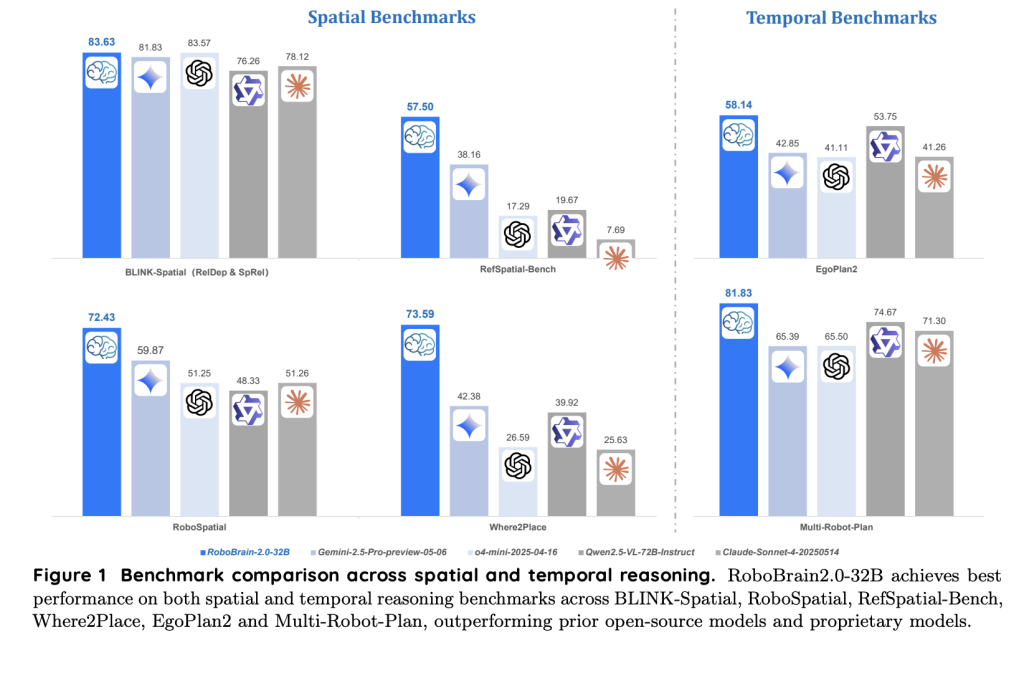
Potential in Embodied AI and Robotics
By unifying vision-language understanding, interactive reasoning, and robust planning, RoboBrain 2.0 sets a new standard for embodied AI. Its modular, scalable architecture and open-source training recipes facilitate innovation across the robotics and AI research community. Whether you are a developer building intelligent assistants, a researcher advancing AI planning, or an engineer automating real-world tasks, RoboBrain 2.0 offers a powerful foundation for tackling the most complex spatial and temporal challenges.
Check out the Paper and Codes. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project | Meet the AI Dev Newsletter read by 40k+ Devs and Researchers from NVIDIA, OpenAI, DeepMind, Meta, Microsoft, JP Morgan Chase, Amgen, Aflac, Wells Fargo and 100s more [SUBSCRIBE NOW]
The post RoboBrain 2.0: The Next-Generation Vision-Language Model Unifying Embodied AI for Advanced Robotics appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ