Visual reasoning tasks challenge artificial intelligence models to interpret and process visual information using both perception and logical reasoning. These tasks span a wide range of applications, including medical diagnostics, visual math, symbolic puzzles, and image-based question answering. Success in this field requires more than object recognition—it demands dynamic adaptation, abstraction, and contextual inference. Models must analyze images, identify relevant features, and often generate explanations or solutions that require a sequence of reasoning steps tied to the visual input.
The limitation becomes evident when models are expected to apply reasoning or modify their strategies for varied visual tasks. Many current models lack flexibility, often defaulting to pattern matching or hardcoded routines. These systems struggle to break down unfamiliar problems or create solutions beyond their preset toolkits. They also fail when tasks involve abstract reasoning or require models to look beyond surface-level features in visual content. The need for a system that can autonomously adapt and construct new tools for reasoning has become a significant bottleneck.
Previous models typically rely on fixed toolsets and rigid single-turn processing. Solutions like Visual ChatGPT, HuggingGPT, or ViperGPT integrate tools like segmentation or detection models, but they are constrained to predefined workflows. This setup limits creativity and adaptability. These models operate without the ability to modify or expand their toolset during a task. They process tasks linearly, which limits their usefulness in domains that require iterative reasoning. Multi-turn capabilities are either missing or severely limited, preventing models from engaging in more in-depth analytical reasoning.
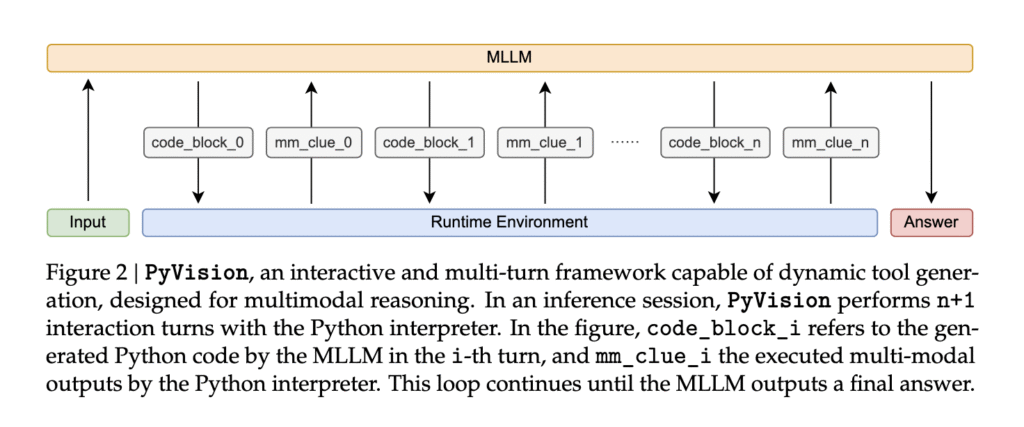
Researchers introduced PyVision to overcome these issues. Developed by teams from Shanghai AI Lab, Rice University, CUHK, NUS, and SII, this framework enables large multimodal language models (MLLMs) to autonomously create and execute Python-based tools tailored to specific visual reasoning problems. Unlike previous approaches, PyVision is not bound by static modules. It uses Python as its primary language and builds tools dynamically in a multi-turn loop. This allows the system to adapt its approach mid-task, enabling the model to make decisions, reflect on results, and refine its code or reasoning across several steps.
In practice, PyVision initiates by receiving a user query and corresponding visual input. The MLLM, such as GPT-4.1 or Claude-4.0-Sonnet, generates Python code based on the prompt, which is executed in an isolated environment. The results—textual, visual, or numerical—are fed back into the model. Using this feedback, the model can revise its plan, generate new code, and iterate until it produces a solution. This system supports cross-turn persistence, which means variable states are maintained between interactions, allowing sequential reasoning. PyVision includes internal safety features, such as process isolation and structured I/O, ensuring robust performance even under complex reasoning loads. It utilizes Python libraries such as OpenCV, NumPy, and Pillow to perform operations like segmentation, OCR, image enhancement, and statistical analysis.
Quantitative benchmarks validate PyVision’s effectiveness. On the visual search benchmark V*, PyVision improved GPT-4.1’s performance from 68.1% to 75.9%, a gain of +7.8%. On the symbolic visual reasoning benchmark VLMsAreBlind-mini, Claude-4.0-Sonnet’s accuracy increased from 48.1% to 79.2%, a 31.1% improvement. Additional gains were observed on other tasks: +2.4% on MMMU and +2.5% on VisualPuzzles for GPT-4.1; +4.8% on MathVista and +8.3% on VisualPuzzles for Claude-4.0-Sonnet. The improvements vary depending on the underlying model’s strengths—models that excel in perception benefit more from PyVision in perception-heavy tasks, while reasoning-strong models gain more in abstract challenges. PyVision amplifies the base model’s abilities rather than masking or replacing them.
This research highlights a substantial advancement in visual reasoning. PyVision addresses a fundamental limitation by enabling models to create problem-specific tools in real-time. The approach transforms static models into agentic systems capable of thoughtful, iterative problem-solving. By dynamically linking perception and reasoning, PyVision takes a critical step toward building intelligent, adaptable AI for complex real-world visual challenges.
Check out the Paper, GitHub Page and Project. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project.
Meet the AI Dev Newsletter read by 40k+ Devs and Researchers from NVIDIA, OpenAI, DeepMind, Meta, Microsoft, JP Morgan Chase, Amgen, Aflac, Wells Fargo and 100s more [SUBSCRIBE NOW]
The post This AI Paper Introduces PyVision: A Python-Centric Framework Where AI Writes Tools as It Thinks appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ