In 2025, agentic AI applications are no longer pet projects—companies around the world are investing in software to incorporate AI agents into their business workflows. The most common use of an AI agent is to assist with research analysis or writing code. LangChain’s recent survey of over 1000 professionals across multiple industries showed that over 51% have already deployed agents in production, with 60% using the agents for research and summarization tasks.
However, leveraging an AI agent for more complex tasks than research and summarization—and implementing them in industrial environments like manufacturing—presents certain challenges.
For example, as new technology is introduced into already established companies, the visibility of brownfield deployments increases. This installation and configuration of new hardware or software must coexist with legacy IT systems. And, while it is easy to run an AI agent in a sandboxed environment, it is harder to integrate agents with machines and Operational Technology (OT) systems speaking industrial protocols like Modbus, PROFINET, and BACnet due to existing legacy infrastructure and an accumulation of tech debt.
To ensure governance and security in industrial environments, data security policies, regulatory compliance, and governance models are essential. Agent profiles with defined goals, rules, responsibilities, and constraints must be established before agents are deployed. Additionally, addressing real-world constraints—like LLM latency—and strategically selecting use cases and database providers can enhance Al agent effectiveness and optimize response times.
What’s more, the successful implementation of AI agents in industrial environments requires a number of foundational elements, including:
Flexible data storage and scalability: An agent requires different types of data to function, such as agent profile, short-term memory, and long-term memory. Industrial AI agents require even more types of data, such as time series data from sensors and PLCs. They require efficient and scalable data storage that adapts to the dynamic needs of the environment.
Continuous monitoring and analysis: An agent deployed in a manufacturing environment requires real-time observability of ever-changing data generated by the factory. It also needs to keep humans in the loop for any critical decisions that might affect production.
High availability: Industrial environments demand near-zero downtime, making system resilience and failover capabilities essential.
XMPro joins forces with MongoDB
To address these challenges, we are pleased to announce XMPro’s partnership with MongoDB. XMPro offers APEX AI, a low-code control room for creating and managing advanced AI agents for industrial applications.
To ensure seamless control over these autonomous agents, XMPro APEX serves as the command center for configuring, monitoring, and orchestrating agent activities, empowering operators to remain in control.
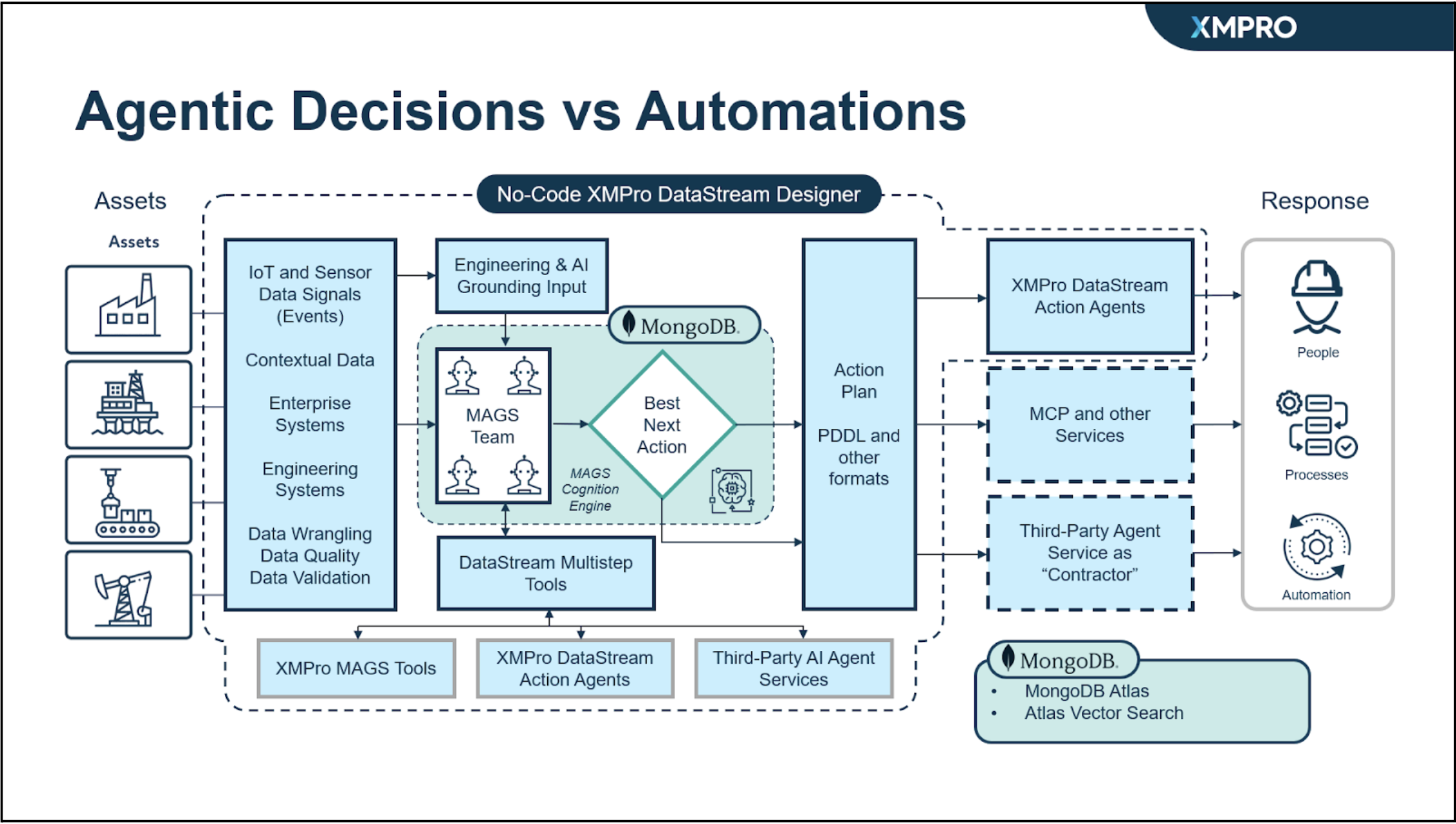
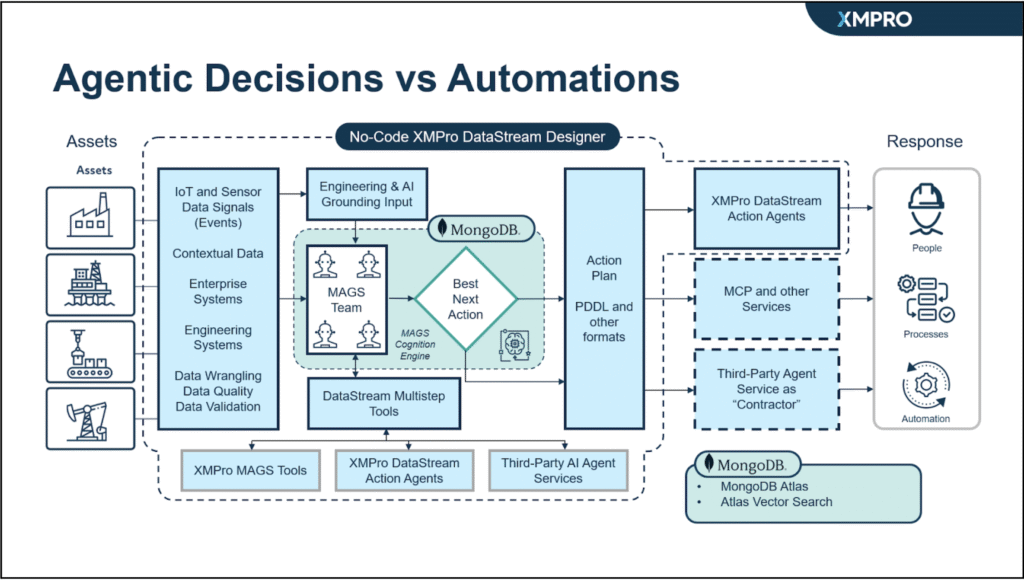
APEX AI, combined with MongoDB Atlas and MongoDB Atlas Vector Search, addresses a variety of challenges faced by developers when building AI agents for industrial environments.
XMPro complements this by seamlessly integrating with industrial equipment such as SCADA systems, PLCs, IoT sensors, and ERPs, enabling continuous monitoring of operations. This integration ensures real-time data acquisition, contextualization, and advanced analytics, transforming raw data into actionable insights. XMPro’s capabilities include condition monitoring, predictive maintenance, anomaly detection, and process optimization, which help reduce downtime and improve operational efficiency while maintaining compliance and safety standards.
XMPro’s industrial AI agents rely on memory persistence for contextual decision-making. MongoDB Atlas acts as the database for storing and retrieving agent memories. Using a flexible document database for storing agentic memories enables agents to store different types of data, such as conversational logs, state transitions, and telemetry data, without requiring schema re-design.
The capabilities of MongoDB Atlas Vector Search empower APEX AI agents with a retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) tool, which helps to reduce LLM hallucinations. This integration allows agents to access and retrieve verified data, grounding their responses. Having database and vector search tools together in MongoDB Atlas also helps reduce agent latency and speeds up development.
APEX AI-enabled multi-agent systems working together in an industrial setting. These context-aware agents can work in tandem, retrieving relevant knowledge stored in MongoDB Atlas to enable meaningful collaboration and better decision-making.
XMPro APEX AI also leverages MongoDB Atlas’s robust security and high availability to ensure that agents can securely access and leverage data in real time; features such as role-based access controls, network isolation, encryption in transit and at-rest are key to why this agent-based AI solution is ideal for securing industrial production environments. MongoDB’s highly available and horizontal scalability ensures seamless data access at scale as organizations scale up their APEX AI deployments.
Unlocking the future of AI in industrial automation
XMPro APEX AI and MongoDB Atlas are a winning combination that paves the way for a new era of industrial automation. By tackling the core challenges of AI agents’ deployment in industrial environments, we’re enabling organizations to deploy robust, intelligent, and autonomous industrial AI agents at scale.
To learn more about MongoDB’s role in the manufacturing industry, please visit our manufacturing and automotive webpage.
Ready to boost your MongoDB skills? Head over to our MongoDB Atlas Learning Hub to start learning today.
Source: Read More