A Knowledge Graph Memory Server allows Claude Desktop to remember and organize information about a user across multiple chats. It can store things like user preferences, past conversations, and personal details. Because the information is saved as a knowledge graph, Claude can understand relationships between different pieces of information. This leads to more personalized responses and reduces repetition — you won’t have to explain the same things again and again.
In this tutorial, we will implement a simple persistent memory using a local knowledge graph in Claude Desktop, to help it remember user information across chats and provide more personalized, consistent responses.
Step 1: Installing the dependencies
Node.js Installation
We’ll be using npx to run the Knowledge Graph Memory Server, and for that, Node.js is required.
- Download the latest version of Node.js from nodejs.org
- Run the installer.
- Leave all settings as default and complete the installation
Claude Desktop Installation
You can download the latest version of Claude Desktop at https://claude.ai/download. Next, you’ll need to configure Claude to connect with your MCP server. To do this, open the claude_desktop_config.json file located in the Claude directory using any text editor. If the file doesn’t exist, go ahead and create it manually.
Step 2: Configuring the mcp.json file
In the mcp.json file, enter the following code:
{
"mcpServers": {
"memory": {
"command": "npx",
"args": [
"-y",
"@modelcontextprotocol/server-memory"
],
"env": {
"MEMORY_PATH": "./memory.json"
}
}
}
}Step 3: Configuring Claude settings
Now, we need to configure Claude so it can use the knowledge graph to create entities, build relationships, and retrieve relevant information.
- Go to File > Settings > Claude Settings > Configure.
- In the Personal Preferences section, add the following text:
(This preference will automatically apply to all conversations.)
Follow these steps for each interaction:
1. User Identification:
- You should assume that you are interacting with default_user
- If you have not identified default_user, proactively try to do so.
2. Memory Retrieval:
- Always begin your chat by saying only "Remembering..." and retrieve all relevant information from your knowledge graph
- Always refer to your knowledge graph as your "memory"
3. Memory
- While conversing with the user, be attentive to any new information that falls into these categories:
a) Basic Identity (age, gender, location, job title, education level, etc.)
b) Behaviors (interests, habits, etc.)
c) Preferences (communication style, preferred language, etc.)
d) Goals (goals, targets, aspirations, etc.)
e) Relationships (personal and professional relationships up to 3 degrees of separation)
4. Memory Update:
- If any new information was gathered during the interaction, update your memory as follows:
a) Create entities for recurring organizations, people, and significant events
b) Connect them to the current entities using relations
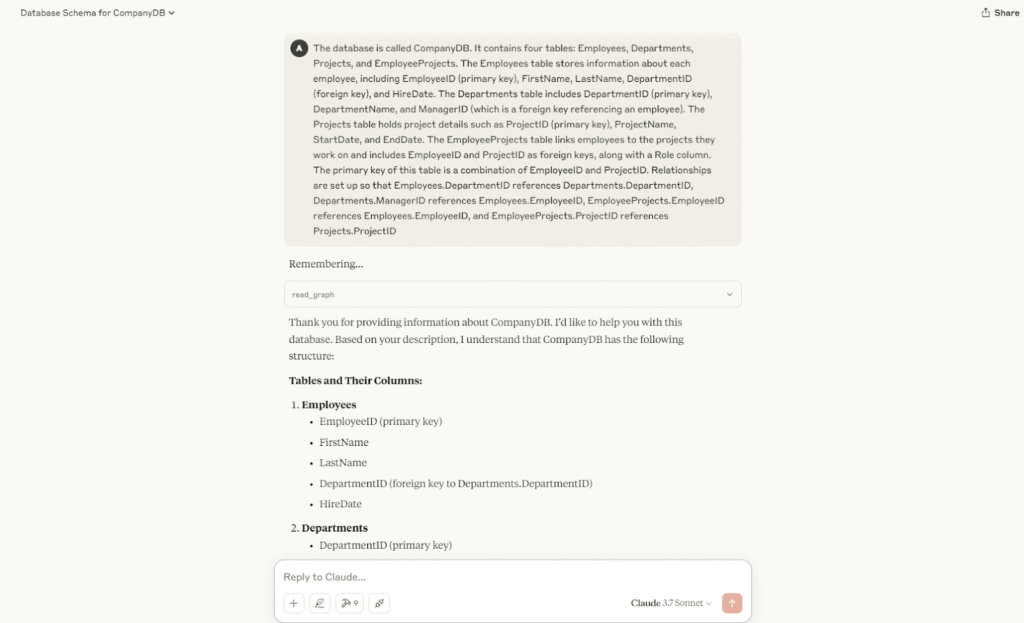
b) Store facts about them as observationsOnce everything is configured, you will see 9 MCP tools available for the Knowledge Graph Server. These tools allow you to: create entities, create relationships, add observations, delete entities, delete observations, delete relationships, read the graph, search nodes, and open nodes.
Additionally, the text we added in the preferences section enables Claude to automatically use these tools during conversations.
Even if we go to a new chat, Claude will remember the information from the previous chats via the knowledge graph. The integration of this MCP tool enhances Claude’s ability to create, modify, and utilize knowledge in real-time, making it a powerful assistant for tasks like database management and SQL query generation. With this memory system in place, Claude becomes a more intelligent, responsive, and consistent tool for all your future interactions. For more details on the knowledge memory server, you can visit this link, where you’ll find resources to help you build even more advanced applications.
Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. Don’t Forget to join our 90k+ ML SubReddit.
The post Implementing Persistent Memory Using a Local Knowledge Graph in Claude Desktop appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ


 [Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on AGENTIC AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 4 Hour Short Event (May 21, 9 am- 1 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop
[Register Now] miniCON Virtual Conference on AGENTIC AI: FREE REGISTRATION + Certificate of Attendance + 4 Hour Short Event (May 21, 9 am- 1 pm PST) + Hands on Workshop