As AI adoption increases in digital infrastructure, enterprises and developers face mounting pressure to balance computational costs with performance, scalability, and adaptability. The rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs) has opened new frontiers in natural language understanding, reasoning, and conversational AI. Still, their sheer size and complexity often introduce inefficiencies that inhibit deployment at scale. In this dynamic landscape, the question remains: Can AI architectures evolve to sustain high performance without ballooning compute overhead or financial costs? Enter the next chapter in NVIDIA’s innovation saga, a solution that seeks to optimize this tradeoff while expanding AI’s functional boundaries.
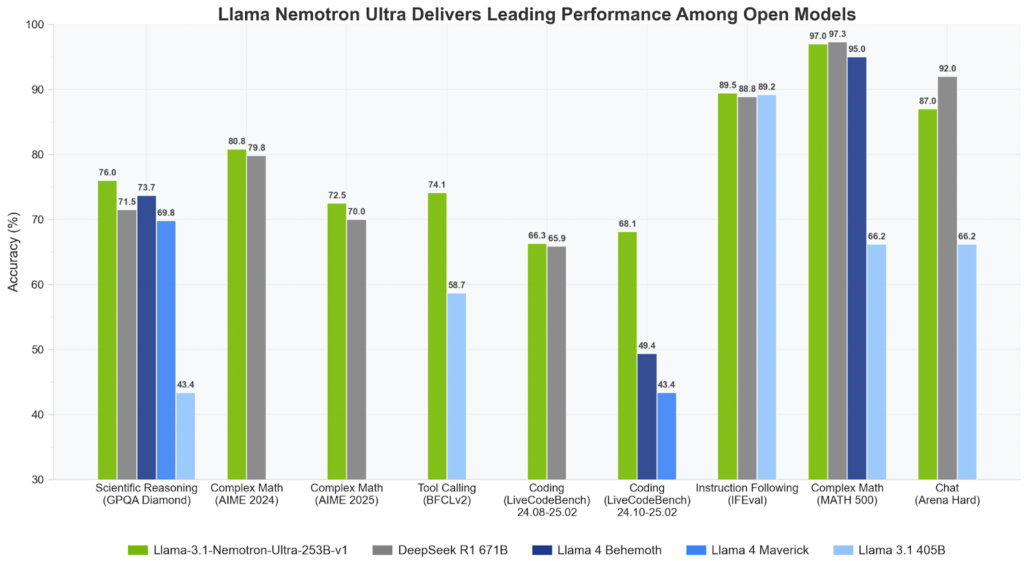
NVIDIA released the Llama-3.1-Nemotron-Ultra-253B-v1, a 253-billion parameter language model representing a significant leap in reasoning capabilities, architecture efficiency, and production readiness. This model is part of the broader Llama Nemotron Collection and is directly derived from Meta’s Llama-3.1-405B-Instruct architecture. The two other small models, a part of this series, are Llama-3.1-Nemotron-Nano-8B-v1 and Llama-3.3-Nemotron-Super-49B-v1. Designed for commercial and enterprise use, Nemotron Ultra is engineered to support tasks ranging from tool use and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) to multi-turn dialogue and complex instruction-following.
The model’s core is a dense decoder-only transformer structure tuned using a specialized Neural Architecture Search (NAS) algorithm. Unlike traditional transformer models, the architecture employs non-repetitive blocks and various optimization strategies. Among these innovations is the skip attention mechanism, where attention modules in certain layers are either skipped entirely or replaced with simpler linear layers. Also, the Feedforward Network (FFN) Fusion technique merges sequences of FFNs into fewer, wider layers, significantly reducing inference time while maintaining performance.
This finely tuned model supports a 128K token context window, allowing it to ingest and reason over extended textual inputs, making it suitable for advanced RAG systems and multi-document analysis. Moreover, Nemotron Ultra fits inference workloads onto a single 8xH100 node, which marks a milestone in deployment efficiency. Such compact inference capability dramatically reduces data center costs and enhances accessibility for enterprise developers.
NVIDIA’s rigorous multi-phase post-training process includes supervised fine-tuning on tasks like code generation, math, chat, reasoning, and tool calling. This is followed by reinforcement learning (RL) using Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO), an algorithm tailored to fine-tune the model’s instruction-following and conversation capabilities. These additional training layers ensure that the model performs well on benchmarks and aligns with human preferences during interactive sessions.
Built with production readiness in mind, Nemotron Ultra is governed by the NVIDIA Open Model License. Its release has been accompanied by other sibling models in the same family, including Llama-3.1-Nemotron-Nano-8B-v1 and Llama-3.3-Nemotron-Super-49B-v1. The release window, between November 2024 and April 2025, ensured the model leveraged training data up until the end of 2023, making it relatively up-to-date in its knowledge and context.
Some of the Key Takeaways from the release of Llama-3.1-Nemotron-Ultra-253B-v1 include:
- Efficiency-First Design: Using NAS and FFN fusion, NVIDIA reduced model complexity without compromising accuracy, achieving superior latency and throughput.
- 128K Token Context Length: The model can process large documents simultaneously, boosting RAG and long-context comprehension capabilities.
- Ready for Enterprise: The model is ideal for commercial chatbots and AI agent systems because it is easy to deploy on an 8xH100 node and follows instructions well.
- Advanced Fine-Tuning: RL with GRPO and supervised training across multiple disciplines ensures a balance between reasoning strength and chat alignment.
- Open Licensing: The NVIDIA Open Model License supports flexible deployment, while community licensing encourages collaborative adoption.
Check out the Model on Hugging Face. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 85k+ ML SubReddit.
The post Nvidia Released Llama-3.1-Nemotron-Ultra-253B-v1: A State-of-the-Art AI Model Balancing Massive Scale, Reasoning Power, and Efficient Deployment for Enterprise Innovation appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ