

Transformer architectures have revolutionized Natural Language Processing (NLP), enabling significant language understanding and generation progress. Large Language Models (LLMs), which rely on these architectures, have achieved remarkable performance across various applications such as conversational systems, content creation, and summarization. However, the efficiency of LLMs in real-world deployment remains a challenge due to their substantial resource demands, particularly in tasks requiring sequential token generation.
A critical issue with LLMs lies in their inference speed, which is constrained by the high memory bandwidth requirements and sequential nature of auto-regressive generation (ARG). These limitations prevent LLMs from being effectively used in time-sensitive applications or on devices with limited computational capacity, such as personal computers or smartphones. As users increasingly demand real-time processing and responsiveness, addressing these bottlenecks has become a priority for researchers and industry practitioners.
One promising solution is Speculative Decoding (SD), a method designed to accelerate LLM inference without compromising generated output quality. SD employs draft models to predict token sequences, which the target model validates in parallel. Despite its potential, the adoption of SD has been hindered by the scarcity of efficient draft models. These models must align with the target LLM’s vocabulary and achieve high acceptance rates, a challenging requirement given the incompatibility issues in existing approaches.
Researchers at Intel Labs introduced FastDraft, an efficient framework for training and aligning draft models compatible with various target LLMs, including Phi-3-mini and Llama-3.1-8B. FastDraft stands out by employing a structured approach to pre-training and fine-tuning. Pre-training focuses on processing datasets containing up to 10 billion tokens of natural language and code while fine-tuning uses sequence-level knowledge distillation to improve draft-target alignment. This process ensures that the draft models achieve optimal performance across diverse tasks.
FastDraft’s architecture imposes minimal requirements, allowing for flexibility in model design while ensuring compatibility with the target LLM’s vocabulary. During pre-training, the draft model predicts the next token in a sequence, using datasets like FineWeb for natural language and The Stack v2 for code. The alignment phase employs synthetic datasets generated by the target model, refining the draft model’s ability to mimic the target model’s behavior. These techniques ensure that the draft model maintains high efficiency and accuracy.
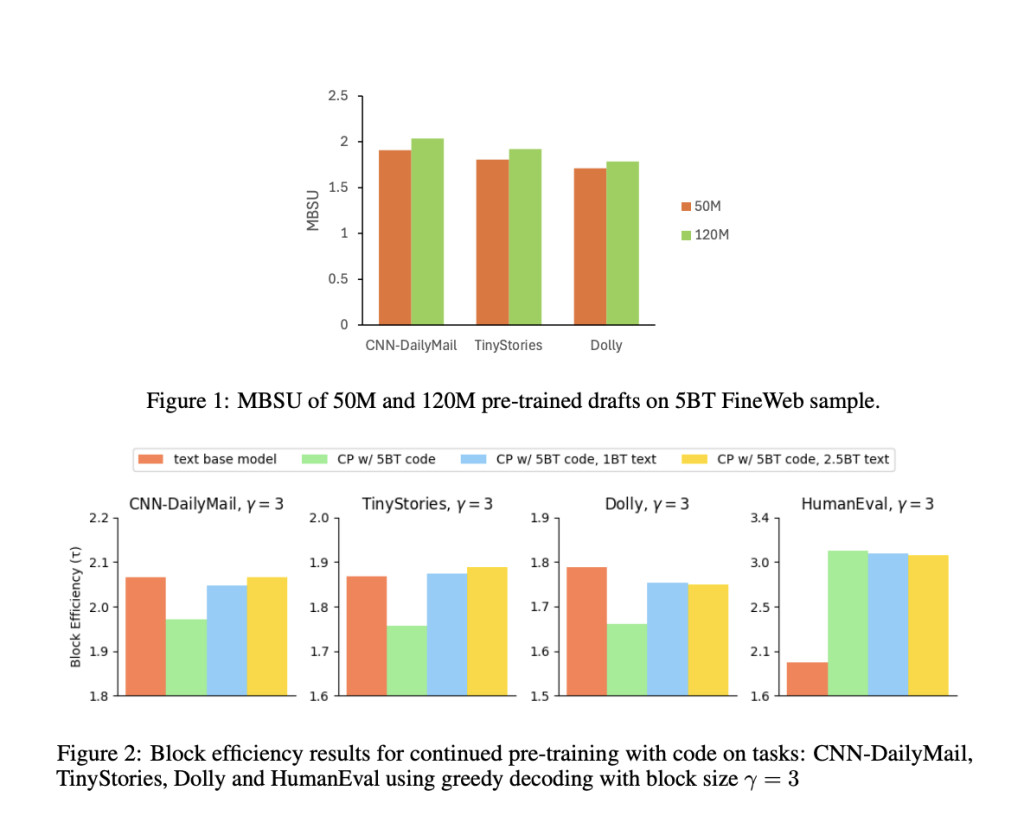
The performance improvements achieved by FastDraft are significant. For instance, the Phi-3-mini draft, trained on 10 billion tokens, achieved a 67% acceptance rate with up to a 3x memory-bound speedup in code tasks. Similarly, the Llama-3.1-8B draft model demonstrated a 2x speedup in summarization and text completion tasks. FastDraft enabled these draft models to be trained on a single server equipped with 8 Intel® Gaudi® 2 accelerators in less than 24 hours. This efficiency makes FastDraft particularly suitable for resource-constrained environments.
The research also provides valuable insights for future LLM draft model training advancements. Key takeaways include:
- Acceptance Rate Improvements: FastDraft achieved a 67% acceptance rate for Phi-3-mini and over 60% for Llama-3.1-8B, reflecting effective alignment with target models.
- Training Efficiency: Training the draft models required less than 24 hours on standard hardware setups, a notable reduction in resource demands.
- Scalability: The framework successfully trained models for various tasks, including code completion and text summarization, using datasets of up to 10 billion tokens.
- Performance Gains: FastDraft delivered up to a 3x memory-bound speedup in code tasks and a 2x improvement in summarization tasks, significantly reducing runtime and memory usage.
- Hardware Adaptability: Benchmarked on Intel® Core
 Ultra processors, the draft models achieved substantial speedups while reducing memory bandwidth demands by up to 3x.
Ultra processors, the draft models achieved substantial speedups while reducing memory bandwidth demands by up to 3x.

In conclusion, FastDraft addresses the critical limitations of LLM inference by introducing a scalable, resource-efficient framework for training draft models. Its innovative methods of pre-training and alignment significantly enhance performance metrics, making it a practical solution for deploying LLMs on edge devices. FastDraft lays a strong foundation for future developments in NLP technology by demonstrating substantial improvements in inference speed and resource efficiency.
Check out the Paper, Model on Hugging Face, and Code on the GitHub Page. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter and join our Telegram Channel and LinkedIn Group. If you like our work, you will love our newsletter.. Don’t Forget to join our 55k+ ML SubReddit.
[FREE AI VIRTUAL CONFERENCE] SmallCon: Free Virtual GenAI Conference ft. Meta, Mistral, Salesforce, Harvey AI & more. Join us on Dec 11th for this free virtual event to learn what it takes to build big with small models from AI trailblazers like Meta, Mistral AI, Salesforce, Harvey AI, Upstage, Nubank, Nvidia, Hugging Face, and more.
The post Intel AI Research Releases FastDraft: A Cost-Effective Method for Pre-Training and Aligning Draft Models with Any LLM for Speculative Decoding appeared first on MarkTechPost.
Source: Read MoreÂ


 Ultra processors, the draft models achieved substantial speedups while reducing memory bandwidth demands by up to 3x.
Ultra processors, the draft models achieved substantial speedups while reducing memory bandwidth demands by up to 3x.